Objective 1.1 Topics:
- Specify a Syslog Server
- Implement and Configure NSX Controllers
- Exclude virtual machines from firewall protection according to a deployment plan
Specify a Syslog Server
We need to configure a syslog server for the NSX Manager. To do that, all we need to do is log into the NSX manager (https://nsxmanager_ip), click on Manage tab and then General.
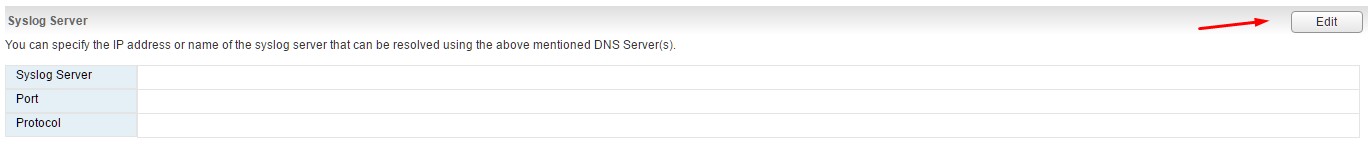
Once there, find the Syslog Server and click Edit.
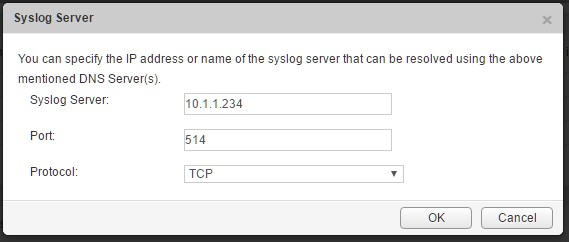
Enter the values for the IP address, port and protocol and click save.
Implement and Configure NSX Controllers
What is an NSX Controller?
NSX controller is the central control point for all logical switches within a network and maintains information of all virtual machines, hosts, logical switches, and VXLANs.
The controller supports two new logical switch control plane modes, Unicast and Hybrid. These modes decouple NSX from the physical network. VXLANs no longer require the physical network to support multicast in order to handle the Broadcast, Unknown unicast, and Multicast (BUM) traffic within a logical switch. The unicast mode replicates all the BUM traffic locally on the host and requires no physical network configuration. In the hybrid mode, some of the BUM traffic replication is offloaded to the first hop physical switch to achieve better performance.
Source: VMware Documentation
Note: Best practices is to deploy the controller in odd groupings. Meaning, we need to deploy the controller count by 1, 3 or 5. If it’s a lab environment you can get away with a single controller. In a production environment, I recommend a minimum of 3.
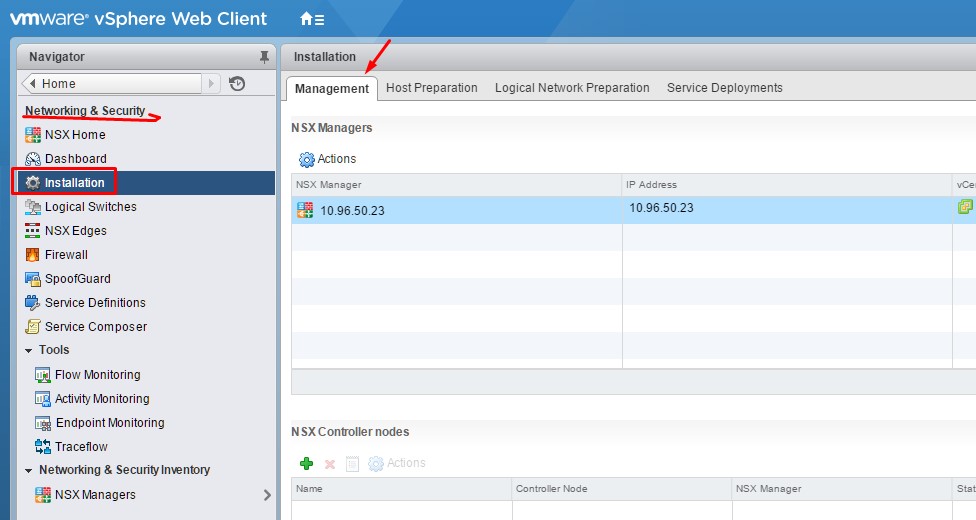
Step 1: Log into the vSphere Web Client and go to Networking & Security and then Installation.
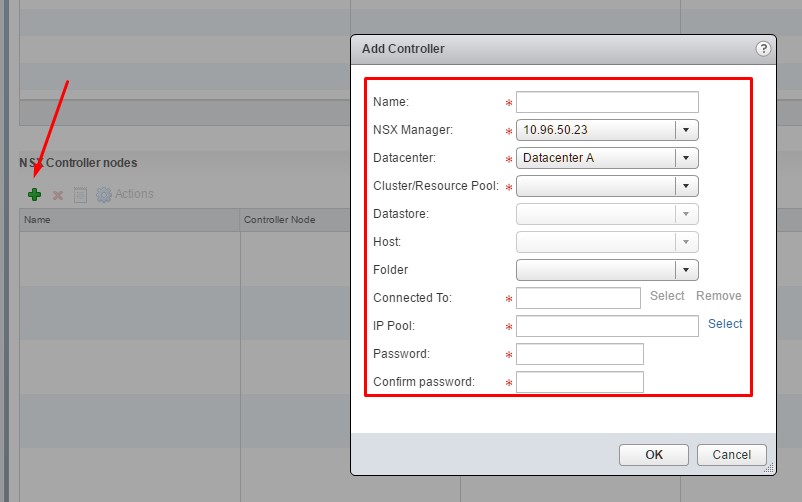
Complete the following fields. You will need to create an IP pool before you can deploy the controllers.
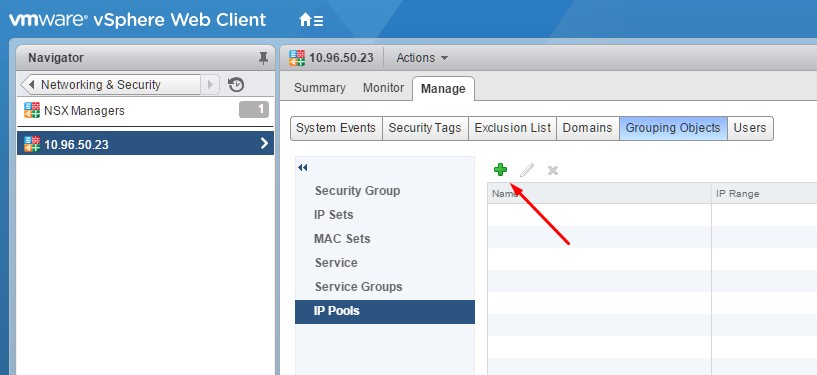
To create an IP Pool:
Navigate to NSX Managers under Networking & Security, select the NSX Manager, Manage tab, Grouping Object and then IP Pools.
Once the IP pool is created, proceed to completing the information for your environment.
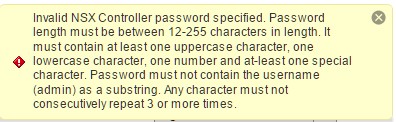
Note: The password requirements differ from most. If you get the following error below, you’ll need to add some complexity to your password.
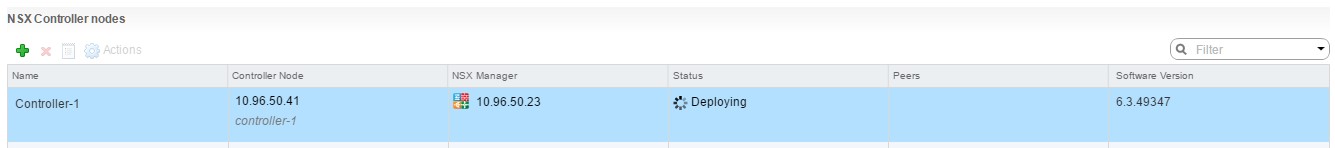
Once done, the first controller will start to be deployed.
If you are deploying more than 1 controller follow the same procedure for additional controllers.
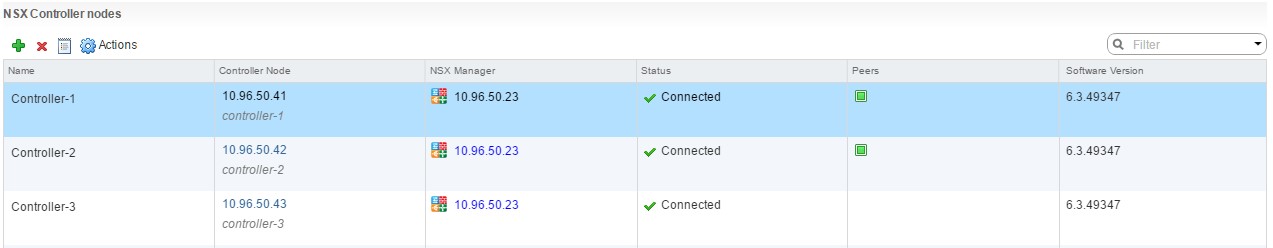
I’ve deployed 3 in my lab environment, as seen below.
Remember, it’s best practice to spread the controllers out across hosts in the cluster for high availability and no single points of failure. You can use DRS affinity & anti-affinity rules to help achieve controller separation.
Exclude virtual machines from firewall protection
You can exclude a set of virtual machines from NSX distributed firewall protection.
NSX Manager, NSX Controllers, and NSX Edge virtual machines are automatically excluded from NSX distributed firewall protection. In addition, VMware recommends that you place the following service virtual machines in the Exclusion List to allow traffic to flow freely.
- vCenter Server. It can be moved into a cluster that is protected by Firewall, but it must already exist in the exclusion list to avoid connectivity issues.
- Partner service virtual machines.
- Virtual machines that require promiscuous mode. If these virtual machines are protected by NSX distributed firewall, their performance may be adversely affected.
- The SQL server that your Windows-based vCenter uses.
- vCenter Web server, if you are running it separately.
Procedure: In the vSphere Web Client, click Networking & Security. Click NSX Managers, select the NSX Manager. Go to the Manage tab, click the Exclusion List tab. Click the Add (green plus) and type the name(s) of the VM’s that you would like exclude and click Add.