Objective 6.1 – Describe a Stretched Cluster Architecture
vSAN stretched clusters provide resiliency against the loss of an entire site. vSAN is integrated tightly with vSphere HA. If a site goes offline unexpectedly, vSphere HA will automatically restart the virtual machines affected by the outage at the other site with no data loss. The virtual machines will begin the restart process in a matter of seconds, which minimizes downtime.
vSAN stretched clusters are also beneficial in planned downtime and disaster avoidance situations. Virtual machines at one site can be migrated to the other site with VMware vMotion. Issues such as an impending storm or rising flood waters typically provide at least some time to prepare before disaster strikes. Virtual machines can easily be migrated out of harm’s way in a vSAN stretched cluster environment.
Things to be aware of:
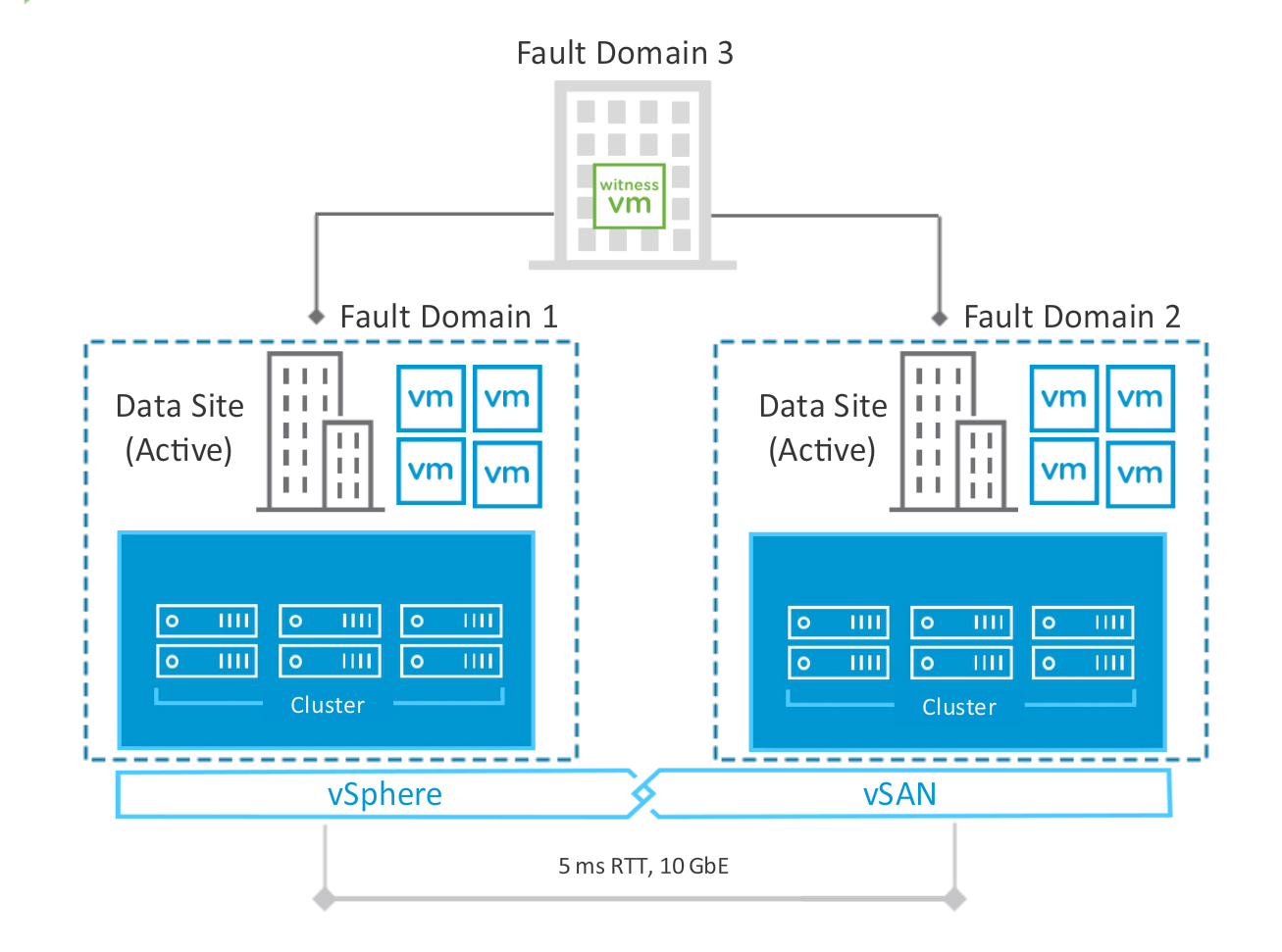
- Support for a maximum of three sites (two data, one witness)
- Each site is configured as a vSAN fault domain
- Identical number of ESXi hosts distributed evenly between the two active/active sites.
- Only one witness host in any stretched clusters configuration
- Across the fault domains, the stretched clusters can have:
- A minimum of two physical hosts (one in each data site) plus a witness host
- A maximum of 30 physical hosts (15 at each data site) plus a witness host
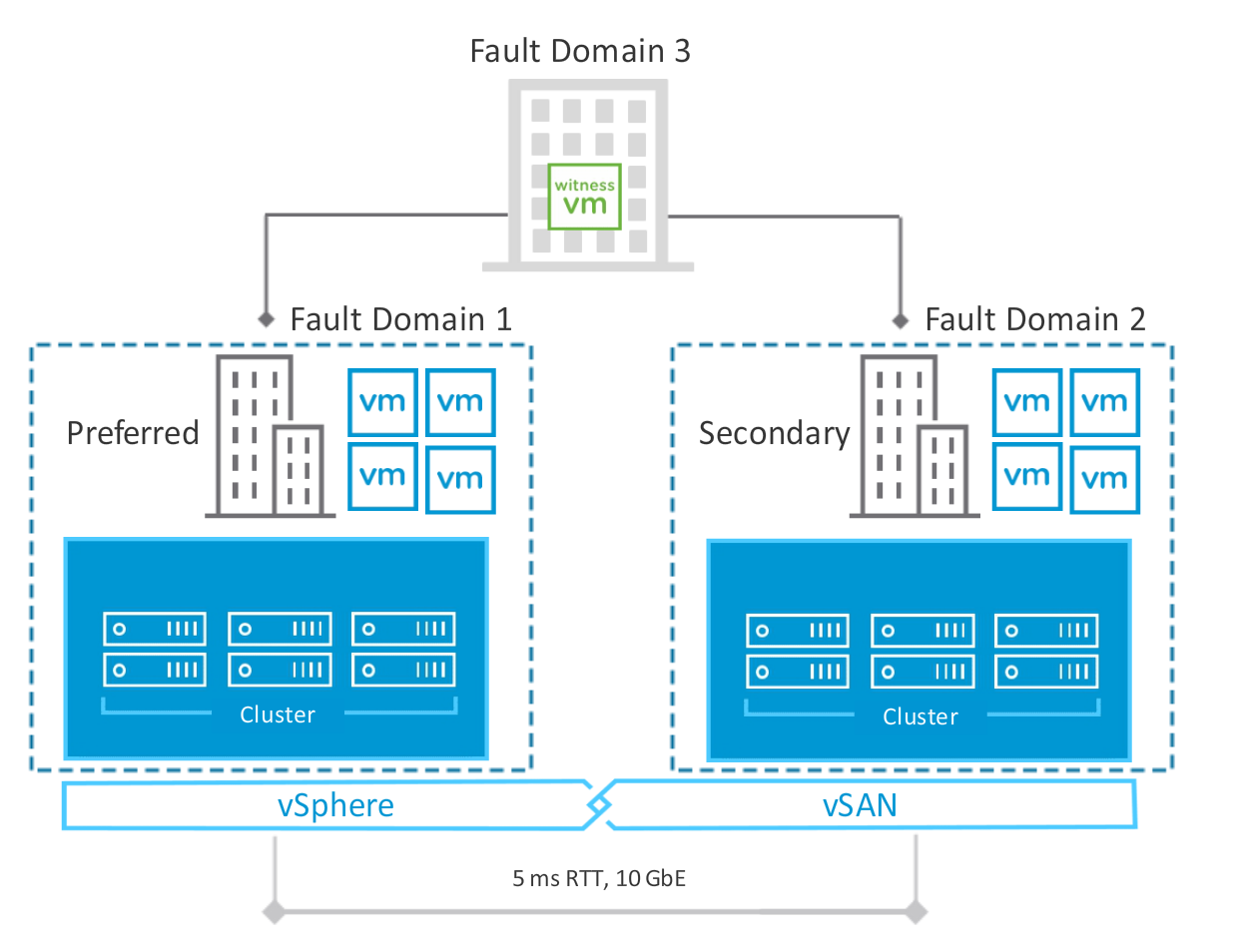
Preferred and Secondary Site of Stretched Clusters
- The preferred site is the data site that remains active when a network partition occurs between the two data sites:
- The other site is known as the secondary site.
- The witness site can still communicate with both data sites.
When the network connectivity returns the two active sites resynchonize between each other.
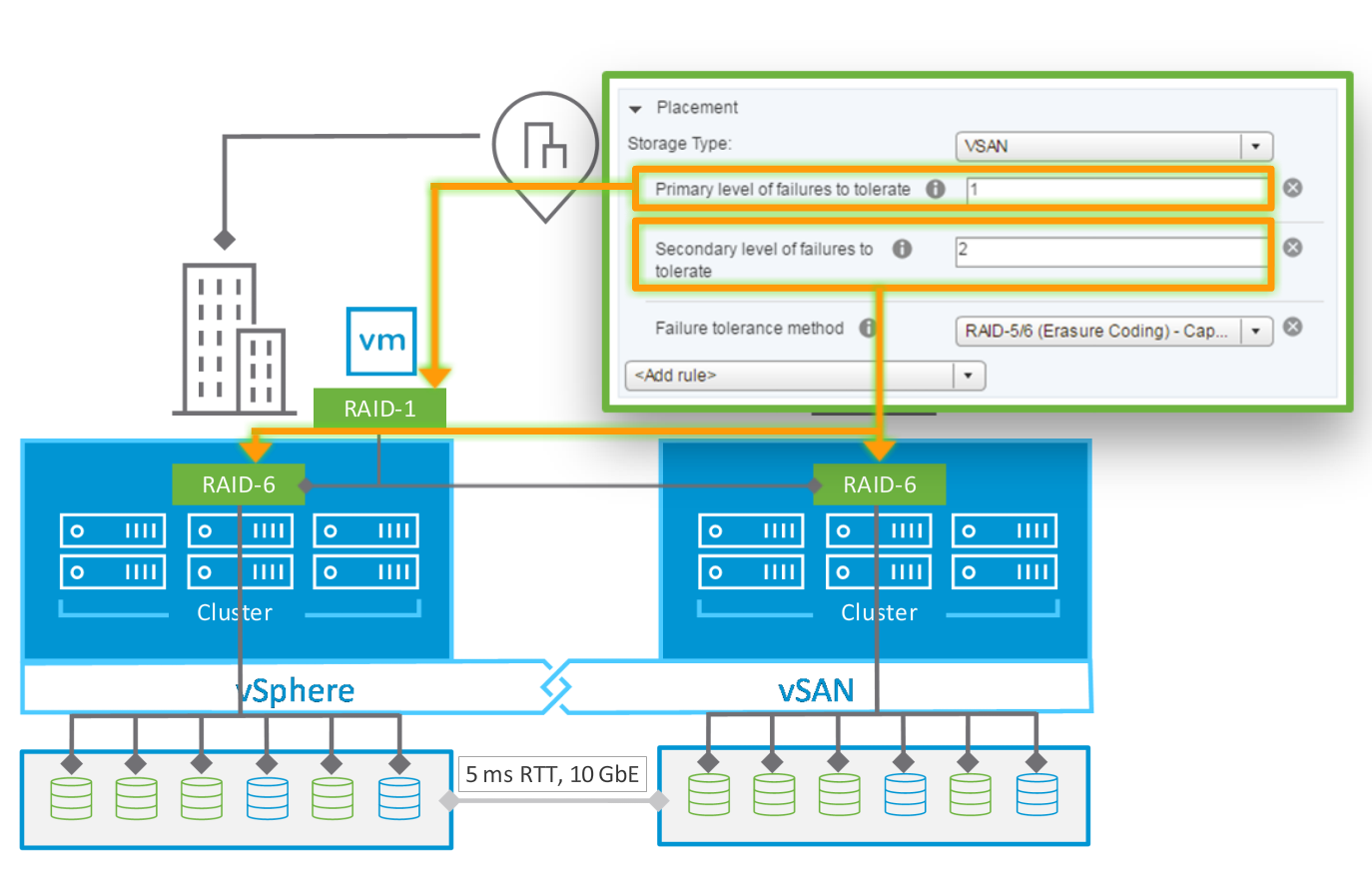
Local and Remote Failure Protection (vSAN 6.6)
- Primary Failures to Tolerate (PFTT) defines the number of sites that can accept failure (0, 1).
- Secondary Failures to Tolerate (SFTT) defines the number within a site that can accept failure (0, 1, 2, 3).
- When a stretched cluster is not configured (PFTT=0), PFTT behaves the same as FTT, and SFTT will NOT be shown as a rule.
- When a stretched cluster is configured (PFTT=1):
- RAID-1 is used to provide replication across two sites.
- Within a site, SFTT dictates if each replica is mirrored (RAID-1) or uses erasure coding (RAID 5/6).
Site Affinity (vSAN 6.6)
If you have VM workload’s that don’t require cross-site protection (such as test/dev) you can have policies (SPBM Polices) that only allow the data to stay in one site in a stretched cluster. Setting the PFTT to 0. One benefit of this new feature is that it helps reduce the network and storage requirements.
Source: VMware vSAN and HCI Fundamentals